Ebike Classes Explained: Find the Perfect Fit for Your Ride
If you ever got confused to figure out key difference among class 1 ebike, class 2 ebike, class 3 ebike and class 4 ebike. Then this article will clear all your confusion.
If you are looking to buy an electric bike or want to ensure that you are not breaking any laws while riding an ebike, then this article is for you.

Understanding eBike classifications will not only help you choose the right electric bike for your needs but also will help you to understand where you can and cannot ride an electric bike based on its class rating.
Over the recent period of time, electric bikes have gained massive popularity in the US and Europe because they are fun to use and convenient. While buying an electric bike we take many factors into consideration, such as age group (for adults, seniors, women, etc.), budget (under $1,000, $2000), and your purpose (for commuting, hunting, adventure, etc). Knowing the class of your ebike is one of them.
Even if you already have an ebike, you should be aware of the class of your ebike. Because you may think that your ebike is allowed on the path that regular analog bikes use, but it may be possible that the class of your bike is prohibited on that particular path, which can lead you to legal trouble.
Jump to
What is an ebike?
According to the definition provided by the California vehicle code, An “electric bicycle” is a bicycle equipped with fully operable pedals and an electric motor of less than 750 watts (i.e., 1 horsepower).
Electric bike classification
Electric bike classification is a basic set of rules that is widely modeled after the California vehicle code, which classifies ebikes into three classes: class 1, class 2, and class 3.
In this article, we will understand the basic differences among them.
This classification is based on parameters such as the wattage of motor, maximum speed assist, and mode of control (i.e., paddle assist or throttle).
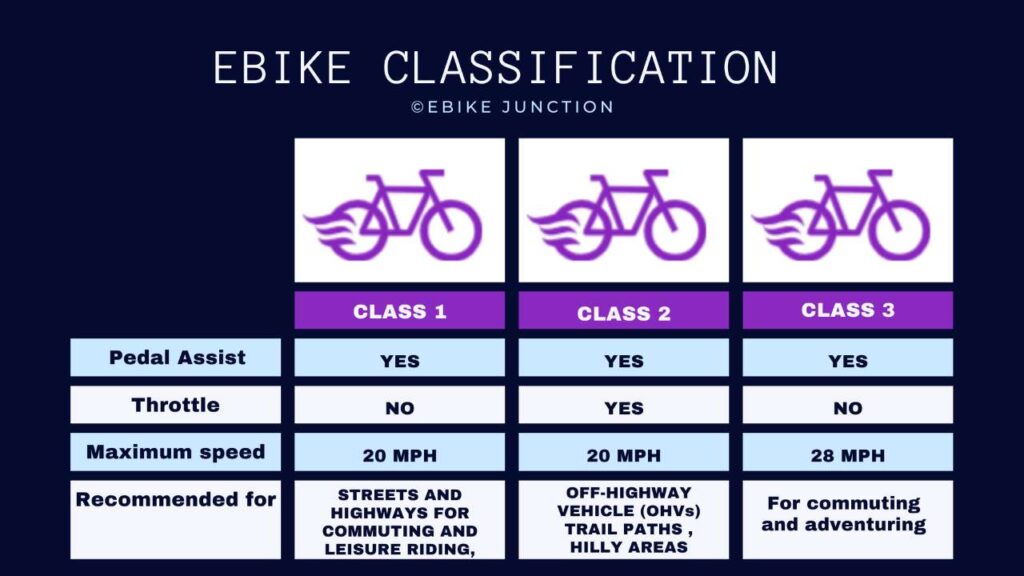
What is a class 1 ebike?
A Class 1 electric bike is an electric bicycle equipped with an electric motor that provides assistance only when the rider is pedaling. It ceases to provide assistance when the bicycle reaches the speed of 20 miles per hour. Class 1 ebikes do not have a throttle.
Class 1 ebikes are also known as ‘Regular street bikes’ or ‘Mountain bikes’. Because it is allowed on streets and highways, lanes, roads, multi-use trails, and bike-only paths.
Pros
Cons
- commuting and leisure riding
- Streets and highways
What is a class 2 ebike?
A “class 2 electric bicycle” is an electric bicycle equipped with an electric motor and throttle, which provide assistance up to the speed limit of 20 miles per hour. Most of the class 2 ebikes offer paddle assist along the throttle.
This means that the rider can ride with the help of throttle without pedaling. However one should keep in mind that as class 2 ebike use throttle as electric assist so the battery consumption will be more rapid.
Pros
Cons
- A person with an injury of limited mobility
- Ideal for hill climbing
- Can be treated as off-highway vehicle
What is a class 3 ebike?
Unlike a Class 1 electric bike, a Class 3 electric bike provides assistance only when the rider is pedaling, and it ceases to provide assistance when the bicycle reaches the speed of 28 miles per hour.
Class 3 electric bikes are usually equipped with a speedometer. They may have or may not be provided with the throttle, which can provide assist up to 20 mph.
Class 3 ebikes are typically allowed on roads and on-road bike lanes (“curb to curb” infrastructure), but restricted from bike trails and multi-use paths. So you must keep in mind local authorities’ rules while riding a class 3 ebilke, because due to its high speed, different states may have their own different rules and regulations regarding it.
Pros
Cons
- Race enthusiastic
- For commuting and adventuring
What is a Class 4 ebike?
Mostly, there are three classes of ebike which are discussed above. However, there is a new emerging class of electric bike—class 4 ebike.
Their motor output is greater than 750 watts and is offered with a combination of paddle assist and throttle. Class 4 ebikes mostly do not have any speed limit.
Class 4 e-bikes actually aren’t considered e-bikes — they’re motor vehicles, just like electric scooters, electric mopeds, or electric motorcycles. As they are treated as motorized vehicles, they need to be licensed and registered.
Find out: Are class 4 ebikes street legal?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What are the different classes of e-bikes?
There are three classes of e-bikes: class 1, class 2, and class 3.
2. How do Class 1 e-bikes perform on hills?
Class 1 e-bikes are good enough for hills as they provide paddle assist up to maximum 20 mph.
3. How is a Class 1 e-bike different from a Class 2 e-bike?
Class 1 e-bikes do not have throttle while class 2 e-bikes do.
4. What is the difference between Class 1 and Class 3 ebike?
The key difference between class 1 and class 3 ebike is the maximum assisted speed limit. Which is 20 mph and 28 mph, respectively.
5. Are Class 2 e-bikes legal on bike paths?
Yes ! They are legal on bike paths.
6. Can Class 3 e-bikes be used on public roads?
Class 3 e-bikes can be used on public roads. However, many places have their own regulations that prohibit class 3 e-bikes from certain paths and trails. The rider must be 16 years older and wear a helmet while riding.
7. Do Class 3 e-bikes require a special license or registration?
No. Class 3 e-bikes do not require a special license or registration as they fall under the category of electric bicycles.
8. Do you need a helmet for a class 3 ebike?
Yes, all riders riding a class 3 ebike must wear helmets.
9. How fast do Class 3 Ebikes go?
Class 3 ebikes are designed in such a way that they provide paddle assist up to a maximum speed limit of 28 miles per hour.
- How fast does a class 4 ebikes go?
There is no maximum speed limit for a class 4 ebikes. It depends on the electric motor output and paddle assist/throttle capacity.
- Which e-bike class is best for beginners?
Class 1 e-bike is best for beginners as it is more convenient and beginner-friendly.
Conclusion :
Understanding e-bike classes is essential for buyers to make the right decisions that align with their legal, safety, and personal riding needs. By knowing the specific characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each class, buyers can choose the right e-bike of their choice that offers the best performance, comfort, and satisfaction for their intended use.
Hopefully, you have now got a better understanding of what is different classes in ebikes. There are so many ebike brands which offer different types of electric bikes based on individual needs and features.
Before buying an electric bike, you must refer to your country or state’s local rules and regulations. Because some regions have restrictions on certain paths and lanes, as well as age restrictions for certain classes of e-bikes. So, understanding these laws is very helpful to ensure that all riders comply with legal requirements.






